Chapter Six: Effects of Hormones on Renal Function
Chapter Six Part One: Effects of Hormones on Renal Function, the opening act (ADH and aldosterone)
Edward Licoricehands
Chapter 6 part 1
In this review of vasopressin, you can find an excellent discussion of basic stimuli and vasopressin receptors: Vasopressin V1a and V1b Receptors: From Molecules to Physiological Systems | Physiological Reviews
X-Linked Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is very rare and there was theory that all patients originated from the same family and traveled to the US on the Hopewell ship JCI - X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus mutations in North America and the Hopewell hypothesis. This report describes another family from the Netherlands with nephrogenic DI including the finding that the urine osmolarity never exceeds 200 mOsm/kg. Hereditary Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus - GeneReviews® (and here’s a family with central diabetes insipidus https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/81/1/192/2649423?login=true )
Although we have all learned that thiazides should be used with diabetes insipidus, to induce mild volume depletion, several case reports and animal data have found that acetazolamide might be the best diuretic for the job. Clinicians from Boston Medical Center tried it out in this report: Acetazolamide in Lithium-Induced Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus | NEJM based on exciting data in mice! https://jasn.asnjournals.org/content/27/7/2082.short
ADH appears to have an effect on potassium excretion. This was investigated by Giebesch who found, with clearance and micropuncture studies in rats plus isolated perfused tubules, ADH increased potassium secretion Influence of ADH on renal potassium handling: A micropuncture and microperfusion study A corollary should be that inhibition of ADH would increase the risk of hyperkalemia but this was not observed in the SALT-1 and SALT-2 trials. 5% of patients developed hyperkalemia in both the tolvaptan group and the placebo group Tolvaptan, a Selective Oral Vasopressin V2-Receptor Antagonist, for Hyponatremia | NEJM
V1 vasopressin as a pressor Exogenous Vasopressin-Induced Hyponatremia in Patients With Vasodilatory Shock: Two Case Reports and Literature Review
We wondered/debated on our observation that hyponatremia is not reliably seen in patients receiving vasopressin in the ICU. In the VASST trial, Vasopressin versus Norepinephrine Infusion in Patients with Septic Shock, 1 patient in each study arm of nearly 400 patients developed hyponatremia. Note that patients with hyponatremia (<130 mEq/L) were excluded from the study.
Excellent review! Vasopressin and the Regulation of Aquaporin-2
This report looks at the PET scan in individuals who are thirsty. Neuroimaging of genesis and satiation of thirst and an interoceptor-driven theory of origins of primary consciousness
Here’s a little discussion of Dr. Grant Liddle. In addition to his eponymous syndrome, he coined the term “ectopic” and developed the dexamethasone suppression test. Grant Liddle (1921–1989) : The Endocrinologist
This is the sad case of licorice gluttony in NEJM which led to hypokalemia and a cardiac arrest. Case 30-2020: A 54-Year-Old Man with Sudden Cardiac Arrest
In this review of the principal and intercalated cells, check out Figure 8 which has an excellent figure of the aldosterone paradox. https://cjasn.asnjournals.org/content/clinjasn/early/2015/01/30/CJN.08880914.full.pdf?with-ds=yes%3Fversioned%3Dtrue
Remarkably, licorice has been used in dialysis patients to lower potassium in patients in this short term trial. Glycyr-rhetinic acid food supplementation lowers serum potassium concentration in chronic hemodialysis patients
Animal studies on pregnant rats demonstrating the reset osmostat as predicted by Roger. Osmoregulation during Pregnancy in the Rat: EVIDENCE FOR RESETTING OF THE THRESHOLD FOR VASOPRESSIN SECRETION DURING GESTATION
Outline: Chapter 6
- Effects of Hormones on Renal Function
- Hormones regulate the kidney
- Some of those hormones come from the kidney
- Other hormones are secreted by the kidney and regulate other processes
- Mechanism of action of hormones
- Generally hormones that affect the kidney do so by either
- Phosphorylation
- Transcription of other protein
- Hormones do this by
- Affecting
- adenylyl Cyclades
- guanylyl cyclase
- Phosphatidylinositol turnover
- Increases intracellular calcium
- Calcium binds to calmodulin
- Calmodulin + calcium triggers phosphorylation events
- Diacylglycerol also increases arachadonic acid a precursor to PGE
- For steroid hormones RNA transcription
- Hormone binds to cytotoxic receptor
- Hormone plus receptor causes conformational change in receptor revealing its DNA binding site
- Describes alternative steroid hormones which have different characteristics in terms of binding to receptors. Example: oxacalcitriol has low affinity for VDBP so more circulates unsound and is rapidly metabolized. Leads to short half life.
- Another example is raloxifene is like estradiol
. Gives beneficial effects of estradiol without promoting endometrial hyperplasia or increasing risk of breast cancer.
- Table 6-1 provides hormones and then lists mechanism
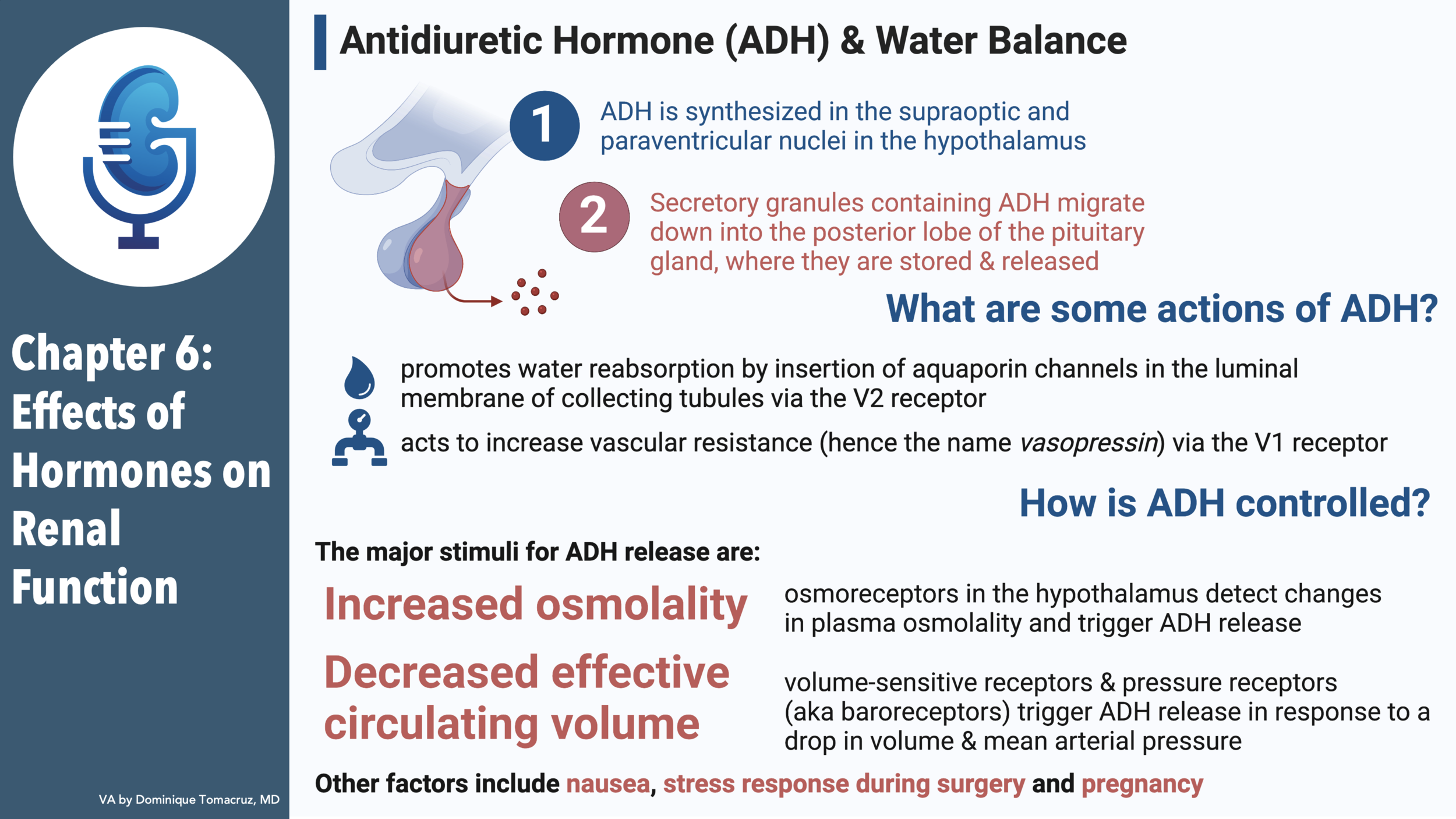
- Antidiuretic Hormone
- Production
- Arginine vasopressin
- Made in supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of hypothalamus
- Migrates down axons to to posterior pituitary
- Some is stored and released from the median eminence
- Half-life is 15-20 minutes
- Maximum diuresis after a water load is 90-120 minutes, enough time to metabolize previously released ADH
- Action
- Determinant of free water excretion
- Increases water permeability in cortical and medullary collecting tubules
- Two receptors
- V1
- This is the vasopressin effect
- Pretty monitor compared to RAAS and SNS
- V2
- This is the water preservation
- Adenylate cyclase linked
- Preformed aqua portion inserted into the membrane, reabsorbed by clathrin coated pits when ADH wears off
- Failure of this system causes NDI
- there is a autosomal recessive form?!
Defect in aquaporin
- V3 or V1b mediates effect of ADH on release of ACTH in pituitary
- Other effects
- Increased K secretion, counters decreased tubular flow from water resorption
- Stimulates renal prostaglandins
- PE seem to retard the water retention effect of ADH
- Seems to be a V1 effect.
- Extra-renal effect
- Regulation of cortisol
- ADH consecrated with CRH
- Cortisol feeds back and inhibits CRH and ADH release
- Adrenal insufficiency stops feedback inhibiting ADH release
- Release of factor VIII and von willer and factor from endothelium
- Good in hemophilia and uremia
- Control
- Stimulated by hyperosmolality and decreased effective circulating volume
- Osmoreceptors
- Experiment of Verney
- Local infusion of hypertonic saline while keeping rest of organism normal osmolality to localize the osmoreceptor
- Hypothalamus has osmoreceptors
- Changes in cell volume depolarize these cells and trigger “ in some way” ADH release
- Glucose is DM acts as an effective osmole and will stim ADH
- Urea changes osm but not tonicity so it does not stim ADH release
- Increment in osm to trigger ADH release is 1%
- Osmotic threshold is 280 to 290
- Role of thirst
- Osmotic stim for thirst is 2-5 point higher than ADH release. Possible it is different osmoreceptors
- Oropharyngeal mechanoreceptors cause satiety after drinking long before change in osm
- Like ADH thirst is also stimulated by volume depletion
- Volume receptors
- Parasympathetic in carotid baroreceptors are important for this
- We call them volume receptors but they are actually pressure receptors and they can give erroneous signals with heart failure
- Insensitive but potent
- Interaction of osmo and volume signals at supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei
- We talk a lot about how hypovolemia is stimulates ADH regardless of osm
- Rose talks about how hyperaldo induces volume overload, which suppresses ADH resulting in the hypernatremia of hyperaldo.
- Other stimuli
- Nausea increase ADH 500-fold
- Pain after surgery causes ADH release
- Pregnancy lowers osmoregulatory stimulus for ADH and
thirst, so there is a lower set point for sodium
- Aldosterone
- Production
- Aldo in zona glomerulosa
- Low concentration of 17 alpha hydroxylase needed to make cortisol and androgens
- Packed with aldosterone synthase
- Aldosterone synthase gene is close to 11-beta hydroxylase on chromosome 8
- Glucocorticoid remedial hypertension happens when ACTH regulated promoter of 11-beta hydroxylase gets grafted onto aldosterone synthase.
- Cortisol, androgens, estrogens in zona fasciculata and reticularis
- Action
- Increase resorbtion of Na, Cl and secretion of K and H
- Figure 6-12 is strange. Do the arrows represent doses of aldo or when aldo infusion starts and when it ends?
- Aldosterone sensitive cells in collecting tubules have 11-beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
- Licorice story
- SAME story
- Co-evolution of 11b hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and aldosterone
- Act at collecting tubules and connecting segment
- Reabsorbed Na but does not secrete K in inner medullary collecting tubule.
- Low salt diet increases Na channels from 100 to 3000
- Increased Na entry means more Na exit on basolateral walls via NaKATPase so plenty of K for secretion
- Nice discussion how you can use amiloride to show that sodium is first
- Intercalated cells have MR also
- “Effect of aldosterone is permissive, since there is little evidence that acid-base balance directly influences aldo release
- Extrarenal effects
- Salivary gland
- Colon
- Sweat
- Control
- Angiotensin II
- Talks about inverse relationship to sodium intake
- Plasma K
- Aldo starts rising as K rises above 3.5
- They act in zona glomerulosa promote conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone and corticosterone to aldostereone
- ACTH has a minor stimulatory effect
- Production of deoxycorticosterone by ACTH is potent mineralocorticoid which negatively feedback
- Aldo stimulated by hyponatremia?
- Maintenance of Na and K balance
- Table 6-3
- Talks about the importance of proximal and loop resorption as well as distal delivery of Na
- Aldosterone escape
- Weight gain of 3 kg
- Spontaneous diuresis
- K loss continues, so sodium loss happens elsewhere in the nephron
- May be regulated by ANP